Innovation Macroprocess

Creating innovation is our mission.
Offering value is our goal.
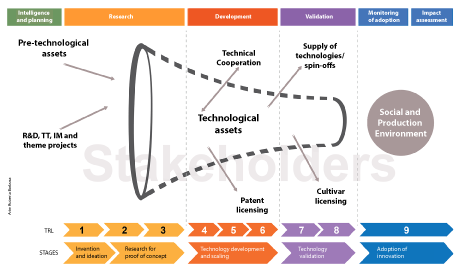
The Innovation Macroprocess is how Embrapa organizes and concatenates its major processes (also understood as stages) to fulfill its mission and deliver value to society. Such major processes are:
1 - Strategic Intelligence and Planning;
2 - Research;
3 - Development and Validation;
4 - Technology Transfer;
5 - Monitoring of Adoption; and
6 - Impact Assessment.
This contrivance makes the results generated by the Corporation more effective and it is based on four focuses:
- Higher connection between research and demands from agriculture.
- Evolution from an individual agenda to a corporate agenda.
- Less dispersion of efforts and resources.
- Increased ability to prioritize.
 Stages of the Innovation Macroprocess
Stages of the Innovation Macroprocess
-
Stage 1: Strategic Intelligence and Planning
It represents the beginning of the Innovation Macroprocess, more precisely in the Unit Planning process. It is at this stage that there should be decisions on, for instance, which flow to follow (research, development/validation or transfer). And, for the sake of adequate planning, the Units need the Corporation's strategic guidelines, which are built in the three initial processes of this stage (Prospecting, Macrostrategy and Corporate Planning). Thus, Corporate Planning establishes strategic goals, innovation challenges (problems and opportunities in the production sector), and contributions and targets for innovation.
-
Stage 2: Research
It covers the generation of pre-technological and technological assets up to level 3 (Proof of Concept) of the TRL/MRL scale. It covers the entire portfolio of Type I projects and part of Type II and III projects.
Several processes run parallel with research, including the structuring of partnerships, fundraising, regulatory matters, intellectual property, and asset qualification.
-
Stage 3: Development and Validation
It starts when an asset reaches level 4 on the TRL scale and covers the entire portfolio of Type II projects and part of Type I and III projects.
Just like in the research stage, different processes run simultaneously (structuring partnerships, fundraising, regulatory matters, intellectual property, and asset qualification).
-
Stage 4: Technology Transfer
It takes place in three situations:
when the company has prioritized a problem or an opportunity for which it already has ready-to-use technology;
when the Research and Development and Validation stages require that knowledge is made available;
when the Research and Development and Validation stages require assets to be qualified and partnerships to be prospectd and formalized (TT sub-processes).
That is, Technology Transfer can be performed after or during the Research and Development and Validation stages. The focus of this stage is to bring the technologies and knowledge by Embrapa and partners closer to adopters to make innovation viable.
-
Stage 5: Monitoring of Adoption
It occurs after Technology Transfer is consolidated, that is, after a given asset is inserted in the market, as target audiences recognize its applicability. The aim is to assess not only adoption variables, but also the asset's technical performance and the relevance of keeping it in the market. The analysis resulting from this stage feeds the other macroprocess flows, especially Strategic Intelligence and Planning, Technology Transfer, and Impact Assessment. Its findings also inform the planning of monitoring, which is cyclically carried out.
-
Stage 6: Impact Assessment
At this stage, the impacts of innovations are assessed and identified. It is an already established process at Embrapa, which follows specific methodology and calendar. The technologies that go through this stage are selected based on the information generated in the previous stage, Monitoring of Adoption.
-
Embrapa Innovation Model
The full implementation of the Innovation Macroprocess requires alliances with public and private organizations in the production sector. The Embrapa Innovation Model focuses on open innovation, which relies on partnerships from the start of the projects to commit to the market insertion of assets.